Anaerobic fermentation technology for animal husbandry
In recent years, China's animal husbandry and farming industries have experienced rapid growth, bringing significant economic benefits to the development of the Ministry of Agriculture. However, at the same time, large amounts of livestock manure and agricultural waste have also caused environmental pollution, which runs counter to China's concept of sustainable development. In response, relevant departments in China have been researching solutions to this issue. Among these, anaerobic fermentation technology for livestock manure has gradually been widely applied due to its technical and economic advantages.
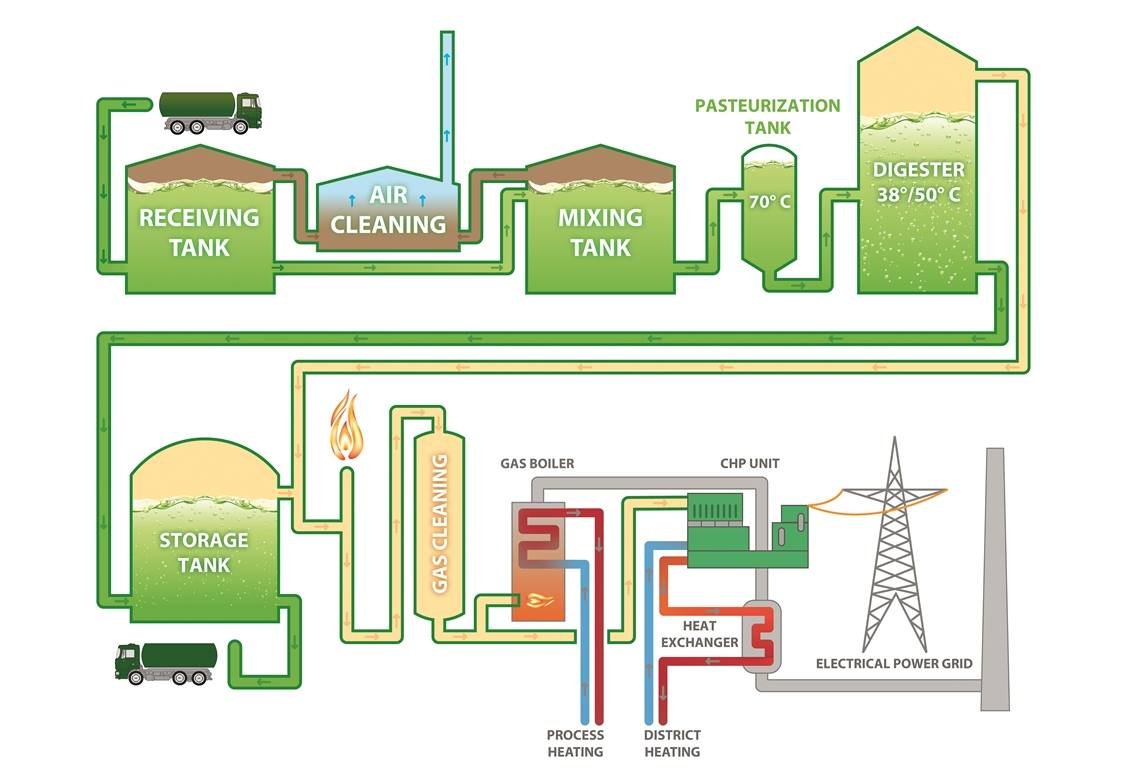
Simple anaerobic fermentation process diagram
Significance of Anaerobic Fermentation
With the continuous development of China's national economy, people's living standards have been steadily improving. The demand for meat, eggs, and dairy products in residents' daily diets has been expanding. This has placed greater demands on China's animal husbandry and farming industries, driving them towards large-scale development. Among the fastest-growing sectors are the pig, cattle, and sheep industries, with the number of large and medium-sized farms across the country having expanded to over 40,000.
While the livestock industry has brought tremendous economic and social benefits, it has also generated large amounts of manure and wastewater, leading to serious water, air, and soil pollution, which poses significant environmental threats. In response to this situation, China has begun exploring various governance methods. Anaerobic fermentation technology, due to its economic and technical advantages, has stood out, with its methane energy production ratio reaching 28.8 MJ/MJ.
Through continuous exploration, China has recognized that although livestock manure contains large amounts of ammonia, phosphorus, and organic matter that pollute the environment, it can also be an excellent resource if properly treated. Anaerobic fermentation technology processes livestock manure to produce biogas, biogas slurry, and biogas residue. Studies have shown that the gas production from different types of livestock manure varies, with the production rate at 55°C being: cow manure > pig manure > chicken manure. The biogas can be used to produce natural gas and generate electricity; the biogas slurry can be used to irrigate farmland; and the biogas residue can be used to produce agricultural fertilizers.
Anaerobic fermentation technology not only produces new energy and provides fertilizers for farmers but also helps manage the environment and reduce pollution, offering substantial overall benefits. The country has also recognized this and explicitly proposed in the "13th Five-Year Plan" to establish large-scale biogas and bio-natural gas projects.
Regardless of the scale, anaerobic fermentation processes consist of several key steps: collecting raw materials, pre-treating these materials, constructing adjustment and digestion tanks, separating solids from liquids after fermentation, separating water from gas, desulfurizing the gas, and storing the fermentation by-products. The basic process is not overly complex.
First, various agricultural wastes are collected, such as livestock manure, discarded straw, and kitchen waste. After mixing the raw materials with wastewater, the first step of treatment is performed, and the mixture is then poured into the adjustment tank. The adjustment tank regulates the temperature and solid content of the raw materials to ensure optimal biogas production during fermentation. The biogas, composed mainly of 15%–60% carbon dioxide and 40%–75% methane, undergoes water and gas separation as well as desulfurization before being appropriately stored for future use.
A portion of the biogas slurry produced during fermentation is returned to the digestion tank to serve as inoculum for the fermentation process, while the remaining slurry is separated into solid and liquid components. The separated biogas residue is an excellent organic fertilizer that can be directly applied to farmland. The remaining biogas slurry can be used for irrigation, thereby achieving true waste utilization.

