Biogas contains hydrogen sulfide gas, which must be removed through desulfurization before combustion and use.
The methane content in biogas is about 55–65%, while in natural gas, it exceeds 90%, making natural gas burn with a stronger flame.
Natural gas has high pressure, while biogas has low pressure. Due to this pressure difference, the stoves and burners used for each are not interchangeable.
There is a significant difference in the methane content between biogas and natural gas.
Typically, biogas contains about 60% methane and around 40% carbon dioxide.
Natural gas is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and non-corrosive. It is mainly composed of methane, but also includes certain amounts of ethane, propane, and heavier hydrocarbons, along with trace amounts of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and sulfur compounds.
Naturally, this results in differences in combustion properties:
Natural gas, due to its high calorific value, large reserves, and wide range of applications, is generally transported as liquefied natural gas (LNG) or via pipelines. However, long-distance transport is particularly costly.
Biogas, on the other hand, is mainly used in rural areas and usually does not require long-distance transport. Additionally, biogas is less stable. Although it is theoretically possible to transport biogas, its composition may change significantly during the process, and its range of applications is limited.
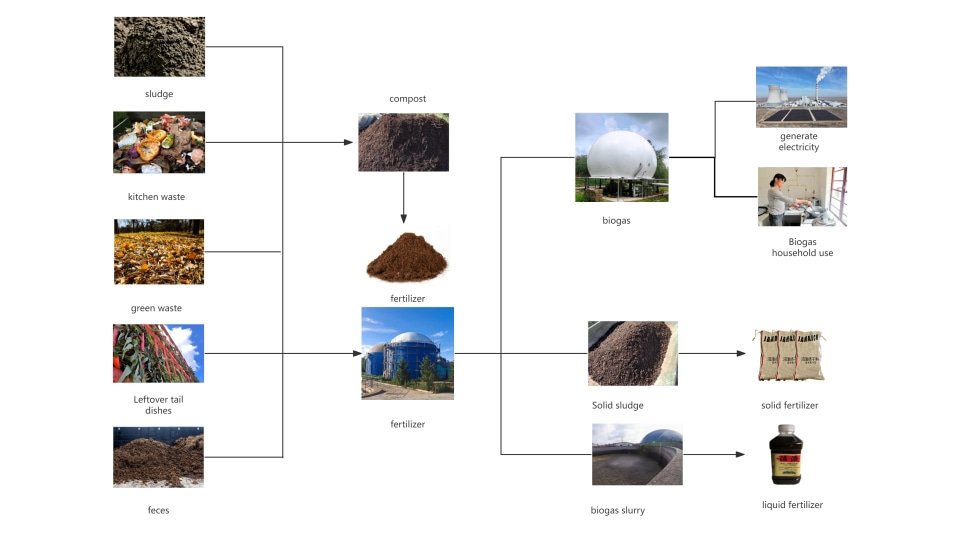
While both natural gas and biogas are combustible gases, they differ significantly in composition, origin, application, and characteristics.
Natural gas is primarily composed of methane, usually over 90%, and also contains small amounts of ethane, propane, and other heavier hydrocarbons. It is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and mainly used for residential and industrial purposes such as heating, power generation, and cooking. Due to its high calorific value and stability, it can be transported over long distances via pipelines or in liquefied form.
Biogas, in contrast, is a mixture of gases produced by the anaerobic digestion of organic matter. Its main components are methane (50%–80%) and carbon dioxide (25%–40%), with small amounts of hydrogen sulfide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and nitrogen. Biogas is generated by placing organic waste like animal manure and crop residues in sealed environments, where microorganisms break down the material. Due to its relatively low methane content and presence of other gases, biogas has a lower combustion efficiency than natural gas and requires desulfurization before use. It is mainly used in rural areas as a supplementary energy source, especially in locations with limited access to electricity and natural gas. However, because it is produced in a decentralized and unstable manner, and its long-distance transport is costly, biogas is difficult to promote on a large scale like natural gas.
Qingdao Haiyue can provide you with biogas solutions. If you have any needs, please feel free to contact us.