Choosing the right roofing material for a gas holder will impact its durability, energy efficiency, and long-term maintenance costs. For double-membrane gas holders, two common single-ply membrane materials are EPDM and PVC. To determine which material is more suitable for your project, it's important to understand their key characteristics.
EPDM vs. PVC Roofing: Key Differences
EPDM and PVC are both polymers, or commonly known as plastics, who are often used in roofing systems. EPDM stands for Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer, which is a type of synthetic rubber. PVC stands for Poly Vinyl Chloride which is a thermoplastic. Meaning it can be melted down and molded, after which it can be cooled, to gain back a solid form.
What is EPDM Roofing?
EPDM roofing is widely used for flat or low-slope roofs and is made from a blend of high-performance synthetic rubber, offering excellent flexibility and durability. EPDM is typically installed in large sheets to reduce the number of seams on the roof, minimizing the risk of leaks. The material is available in black or white and is capable of withstanding various weather conditions, including UV radiation and extreme temperatures.
What is PVC Membrane Roofing?
PVC roofing is a type of single-ply roofing membrane used primarily for low-slope or flat roofing materials. Made from a durable thermoplastic material, PVC is known for its strong resistance to chemicals, fire, punctures, and harsh weather conditions. Available in white or light colors, PVC is highly reflective. PVC roofing systems are heat-welded at the seams, creating a watertight bond that enhances durability and leak prevention.

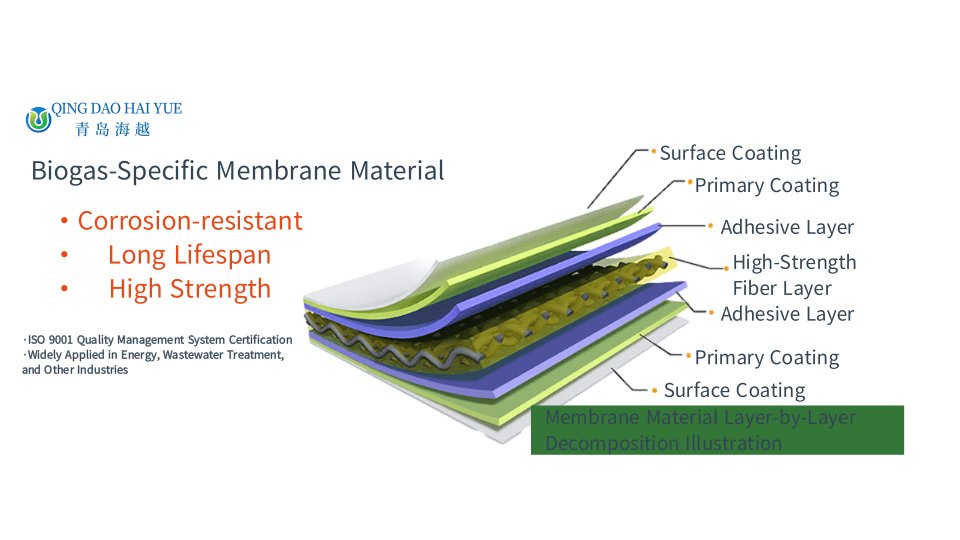
Pros of EPDM Roofing
Durability: EPDM roofing is renowned for its exceptional durability, capable of withstanding extreme temperatures, UV radiation, and moisture in various environmental conditions.
High Flexibility: In cold environments, EPDM remains flexible and does not crack due to the thermal expansion and contraction of the building structure.
Fewer Seams, Reduced Leak Risk: EPDM is typically installed in large sheets, reducing the number of seams, speeding up the installation process, and lowering the risk of leaks.
Low Maintenance Cost: After installation, EPDM requires only occasional inspections and minor repairs, making maintenance simple.
Environmentally Sustainable: EPDM is made from recyclable materials and can be fully reused at the end of its life cycle.
Cost-Effective: The cost of EPDM roofing ranges from $4 to $14 per square foot, making it relatively affordable.
Cons of EPDM Roofing
Heat Absorption: EPDM is typically black, which can absorb heat and cause the roof temperature to rise. Although white EPDM is available to reflect sunlight and reduce heat buildup, it is less commonly chosen.
Vulnerable to Punctures: Despite its overall durability, EPDM is susceptible to punctures from sharp objects, which can lead to leaks and require timely repairs.
Installation Challenges: EPDM is installed using adhesives, and if not applied properly or if the adhesive degrades over time, it may cause seam failure and lead to water infiltration.
Limited Compatibility: EPDM may not be compatible with all roof coatings or sealants, which limits repair options and adds complexity to maintenance.
Slippery Risk: The surface of EPDM can become slippery when wet, posing a safety hazard for individuals performing maintenance or inspections, particularly on sloped roofs.

Pros of PVC Roofing
Durability: PVC roofing has a lifespan of 20 to 30 years, offering high long-term reliability.
Fire Resistance: PVC has fire-retardant properties that effectively reduce the risk of fire spreading across the roof.
Energy Efficiency: PVC is typically white or light-colored, which reflects sunlight, reduces heat absorption, lowers cooling costs, and improves the building's energy efficiency.
Superior Waterproofing: PVC roofing uses heat-welded seams to form a waterproof seal, significantly reducing the risk of leaks and enhancing durability.
Low Maintenance Cost: Once installed, PVC requires minimal maintenance, providing high cost-effectiveness in the long run.
Versatility: PVC roofing has good flexibility and can adapt to various roof shapes, making it widely applicable.

Cons of PVC Roofing
High Initial Cost: PVC roofing has a high initial cost, ranging from $4 to $15 per square foot.
Installation Requirements: PVC roofing requires precise installation; improper installation can lead to seam failure or water infiltration.
Environmental Concerns: The production of PVC involves chlorine and other chemicals, which may have an environmental impact.
Vulnerable to Punctures: Despite its durability, PVC is still susceptible to punctures from sharp objects, which can lead to leaks.
Aging Risk: Over time, PVC membranes may shrink, increasing stress on seams and waterproof layers, leading to potential structural failures.
Material Brittleness: The plasticizers in PVC gradually migrate out of the material, causing it to become brittle and more prone to cracking as it ages.